Sending POST data to php using angular 16 - Codzify
Article by: Manish Methani
Last Updated: September 13, 2021 at 8:04am IST
Table of Contents:
Final Output
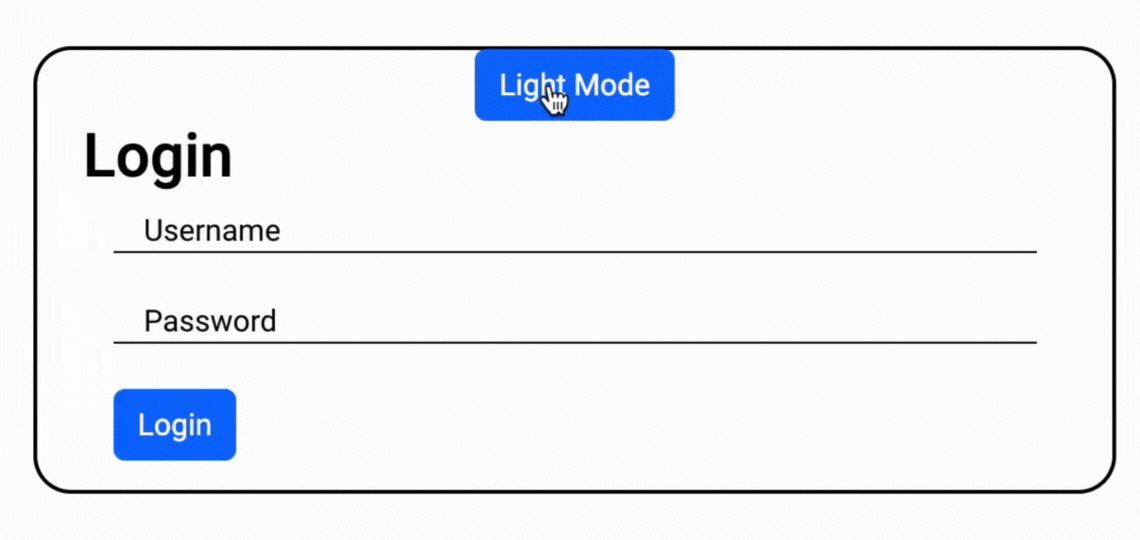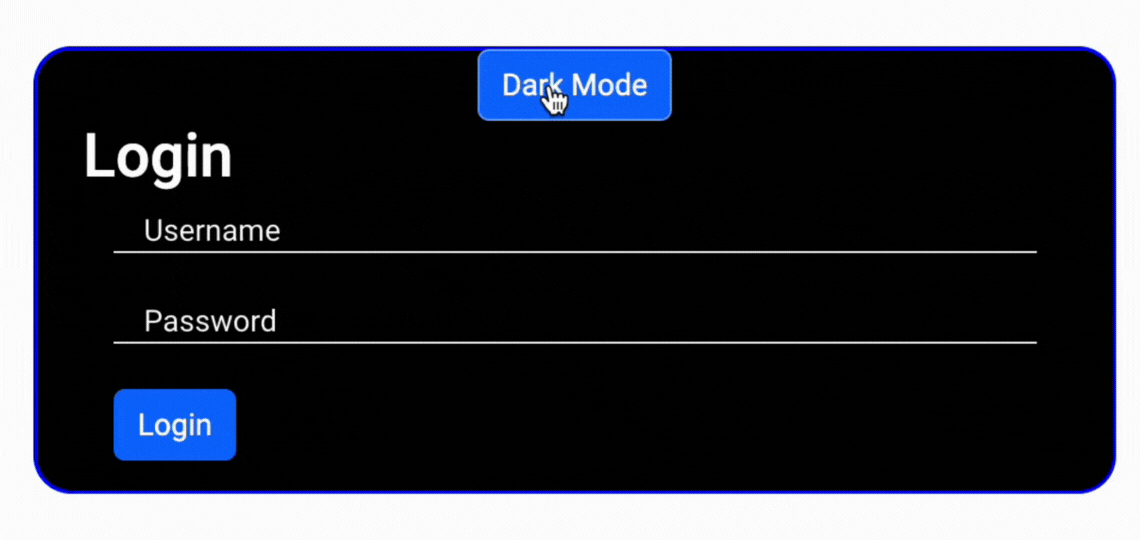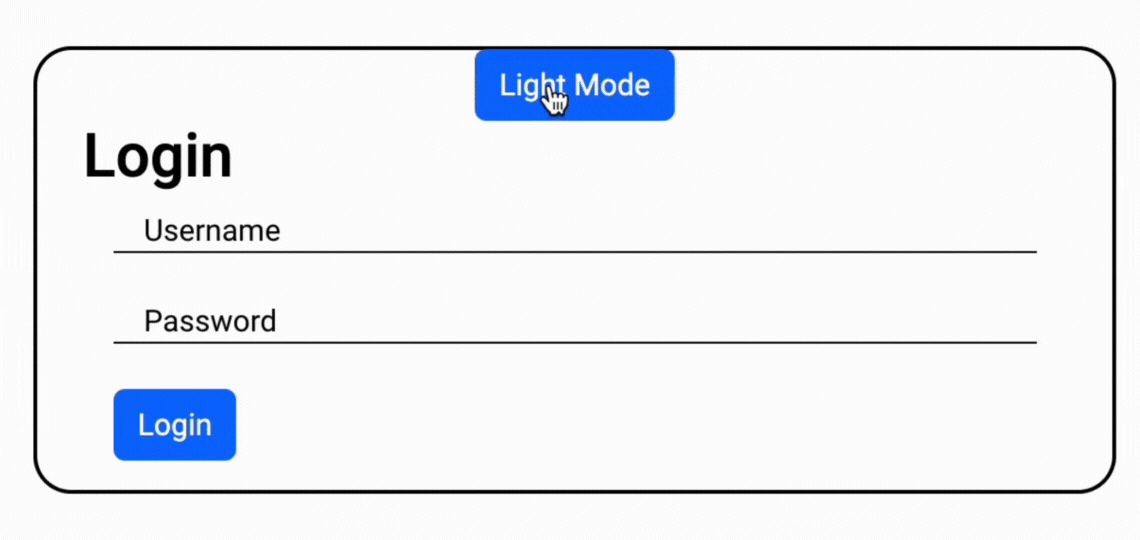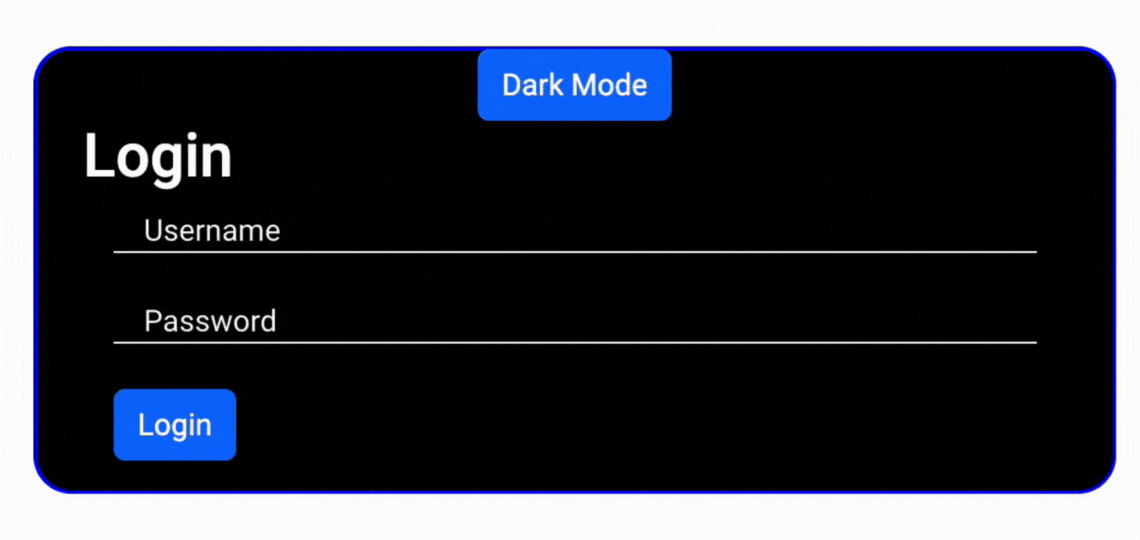
Sending data from an Angular application to a PHP server is a common task when developing web applications. In this tutorial, we will walk through the process of creating an Angular application to send POST data to a PHP backend server. We'll cover both the Angular frontend and the PHP backend handling to handle create operations.
Prerequisites
Before we dive into the code, make sure you have Angular 16 and Angular Material installed in your project. You can set up a new project using the Angular CLI:
sudo npm install -g @angular/cli
sudo ng new dynamic-css-demo
cd dynamic-css-demo
ng add @angular/material
npm install
During the Angular CLI prompts, select the default options.
Generate a Dynamic Styling Component:
Use the Angular CLI to generate a new component for the login box:
ng generate component dynamic-styling
Create API Service
ng generate service api
This command will create api.service.ts file for you. Now inside this file add the following code,
import { Injectable } from "@angular/core";
import { HttpClient } from "@angular/common/http";
import { Observable } from "rxjs";
@Injectable({
providedIn: "root"
})
export class ApiService {
private baseUrl = "https://website.com/fileName.php"; // Replace with your PHP API URL
constructor(private http: HttpClient) {}
// Select operation
getRecords() {
const apiUrl = "https://website.com/fileName.php";
return this.http.get(apiUrl);
}
sendFormData(formData: FormData) {
const apiUrl = "https://website.com/fileName.php";
return this.http.post(apiUrl, formData);
}
// Update operation
updateRecord(id: number, updatedData: any) {
const apiUrl = `https://website.com/fileName.php?id=${id}`;
return this.http.put(apiUrl, updatedData);
}
// Delete operation
deleteRecord(id: number) {
const apiUrl = `https://website.com/fileName.php?id=${id}`;
return this.http.delete(apiUrl);
}
}
Designing HTML File
Open dynamic-styling.component.html file and add the following codde,
<div class="login-container" [ngStyle]="loginStyles">
<button class="btn bg-primary text-white" color="accent" (click)="toggleStyles()">{{buttonText}}</button>
<h2>Register</h2>
<form (ngSubmit)="sendData()">
<mat-form-field class="full-width">
<input matInput [(ngModel)]="newUser.name" name="name" placeholder="Username">
</mat-form-field>
<mat-form-field class="full-width">
<input matInput [(ngModel)]="newUser.email" name="email" type="password" placeholder="Password">
</mat-form-field>
<button type="submit" class="btn bg-primary text-white" color="primary">Register</button>
</form>
</div>
Handling the Methods
Open dynamic-styling.component.ts file and add the following code to sendData to PHP code with the help of APIService ,
import { Component, Renderer2, ElementRef } from "@angular/core";
import { ApiService } from "../api.service";
import { HttpClient } from "@angular/common/http";
import { Observable } from "rxjs";
@Component({
selector: "app-dynamic-styling",
templateUrl: "./dynamic-styling.component.html",
styleUrls: ["./dynamic-styling.component.css"]
})
export class DynamicStylingComponent {
users: any[] = [];
newUser: any = {};
successMessage: string = "";
buttonText = "Dark Mode";
constructor(private renderer: Renderer2, private apiService: ApiService, private http: HttpClient) {}
ngOnInit(): void {
this.apiService.getRecords().subscribe((data: any) => {
this.users = data;
});
}
sendData(): void {
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append("name", this.newUser.name);
formData.append("email", this.newUser.email);
const apiUrl = "https://codzify.com/AdminModule/Admin/resource.php";
this.apiService.sendFormData(formData).subscribe(
(response: any) => {
// Handle the success response here
this.successMessage = response.message;
alert(this.successMessage);
this.newUser = {}; // Clear the form
},
(error: any) => {
// Handle the error response here
console.error(error);
}
);
}
loginStyles: { [key: string]: string } = {
"background-color": "black",
"border": "2px solid blue",
"color": "white",
"margin":"30%",
"margin-top": "10%",
"height": "30%",
"border-radius": "20px"
};
toggleStyles() {
if (this.loginStyles["background-color"] === "black") {
this.loginStyles["background-color"] = "white";
this.loginStyles["border"] = "2px solid black";
this.loginStyles["color"] = "black";
this.buttonText = "Light Mode"; // Change the button text to "Light Mode"
} else {
this.loginStyles["background-color"] = "black";
this.loginStyles["border"] = "2px solid blue";
this.loginStyles["color"] = "white";
this.buttonText = "Dark Mode"; // Change the button text to "Light Mode"
}
}
}
Setting up the PHP Backend
Next, let's create a PHP backend to receive data from the Angular application and perform database operations.
1. Create a PHP file In your PHP server environment, create a PHP file named resource.php. This file will handle requests from the Angular app. Here is a basic example of how resource.php can be structured to handle create, update, delete, and select operations:Also create a newTable named as "resource" and add the three fields: id, name & email.
<?php
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
header("Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods: POST, GET, PUT, DELETE");
header("Access-Control-Max-Age: 3600");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Content-Type, Access-Control-Allow-Headers, Authorization, X-Requested-With");
// Include your config file and any other necessary dependencies
require_once "database.php";
// Initialize the session or any other initialization as needed
// Check if the request method is POST and data is not empty
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] === "POST" && !empty($_POST)) {
// Get user data from the POST request
$name = $_POST["name"];
$email = $_POST["email"];
// Initialize the response array
$response = array();
// Prepare an insert statement
$sql = "INSERT INTO resource (name, email) VALUES (?, ?)";
if ($stmt = mysqli_prepare($con, $sql)) {
// Bind variables to the prepared statement as parameters
mysqli_stmt_bind_param($stmt, "ss", $param_name, $param_email);
// Set parameters
$param_name = $name;
$param_email = $email;
// Attempt to execute the prepared statement
if (mysqli_stmt_execute($stmt)) {
// User inserted successfully
$response["message"] = "User inserted successfully";
http_response_code(201); // Created
} else {
// Error occurred while inserting
$response["message"] = "Something went wrong. Please try again later.";
http_response_code(503); // Service Unavailable
}
// Close the prepared statement
mysqli_stmt_close($stmt);
} else {
// Error in preparing the statement
$response["message"] = "Statement preparation failed.";
http_response_code(503); // Service Unavailable
}
// Close the database connection
mysqli_close($con);
// Send the response as JSON
echo json_encode($response);
} else {
// Invalid request method or empty data
http_response_code(400); // Bad Request
echo json_encode(array("message" => "Invalid request"));
}
?>Testing the Application
With both the Angular frontend and the PHP backend set up, you can start testing the application. Run the Angular app using the following command:
ng serve
You can access the app at http://localhost:4200.
Ensure your PHP server is running and that the PHP file is in the correct location.
You can now createusers using the Angular app, and the data will be sent to the PHP backend.
Final Output

Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to create an Angular application that communicates with a PHP backend to send POST data. This combination of Angular and PHP provides a foundation for building more complex web applications that require data interaction between the frontend and the backend.
FAQ
1. What is Angular 16 and how can I send POST data to a PHP server using it?
Angular 16 is the latest version of the Angular framework. To send POST data to a PHP server using Angular 16, you can follow these steps:
- Set up your Angular 16 project and create a component for your form.
- Design your form in the components HTML file and use Angulars two-way data binding to capture user input.
- Create a method in your component that will be triggered when the form is submitted. Inside this method, use Angulars HTTP client to send a POST request to your PHP server.
- In your PHP script, handle the incoming POST data, process it, and send back a response.
2. What are the advantages of sending data from an Angular 16 application to a PHP server?
Sending data from an Angular 16 application to a PHP server offers several advantages, including:
- Server-Side Processing: PHP is a server-side scripting language, making it suitable for handling data securely on the server.
- Data Persistence: PHP can store and retrieve data from databases, ensuring data persistence.
- Scalability: PHP server-side processing allows your application to scale as needed.
- Integration: PHP can be integrated with various databases and services, enhancing the functionality of your application.
3. What is the role of the PHP script in the data submission process?
The PHP script plays a crucial role in the data submission process from an Angular 16 application. It serves as the server-side endpoint that receives, processes, and stores the data sent by the Angular application. The PHP script handles data validation, interacts with databases if necessary, and sends back a response to the Angular application, confirming the successful data submission or reporting any errors.
4. What security considerations should I keep in mind when sending POST data to a PHP server from Angular 16?
When sending POST data to a PHP server from Angular 16, it is important to consider security. Some key security considerations include:
- Data Validation: Validate data on both the client-side (Angular) and server-side (PHP) to prevent malicious input.
- Use HTTPS: Ensure data transmission is secure by using HTTPS to encrypt the communication between the Angular application and the PHP server.
- Authentication and Authorization: Implement user authentication and authorization to restrict access to sensitive data and actions.
- SQL Injection Prevention: If using databases, use parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection attacks.
5. How can I handle errors and exceptions when sending data from Angular 16 to a PHP server?
Handling errors and exceptions when sending data from Angular 16 to a PHP server is essential for a robust application. Consider the following steps:
- Client-Side Error Handling: Implement error handling in your Angular application to provide user-friendly error messages and gracefully handle client-side issues.
- Server-Side Error Handling: In your PHP script, use try-catch blocks to capture and handle exceptions. Log errors for debugging purposes.
- HTTP Status Codes: Use appropriate HTTP status codes in your PHP responses to indicate success or failure (e.g., 200 for success, 4xx for client errors, and 5xx for server errors).
P.S.: If you are interested in learning Angular 16 in-depth, I have packaged my knowledge in this Angular course. Start your free Trial
