Mastering Inheritance in C++: Types and Examples Explained
Article by: Manish Methani
Last Updated: October 16, 2021 at 2:04pm IST
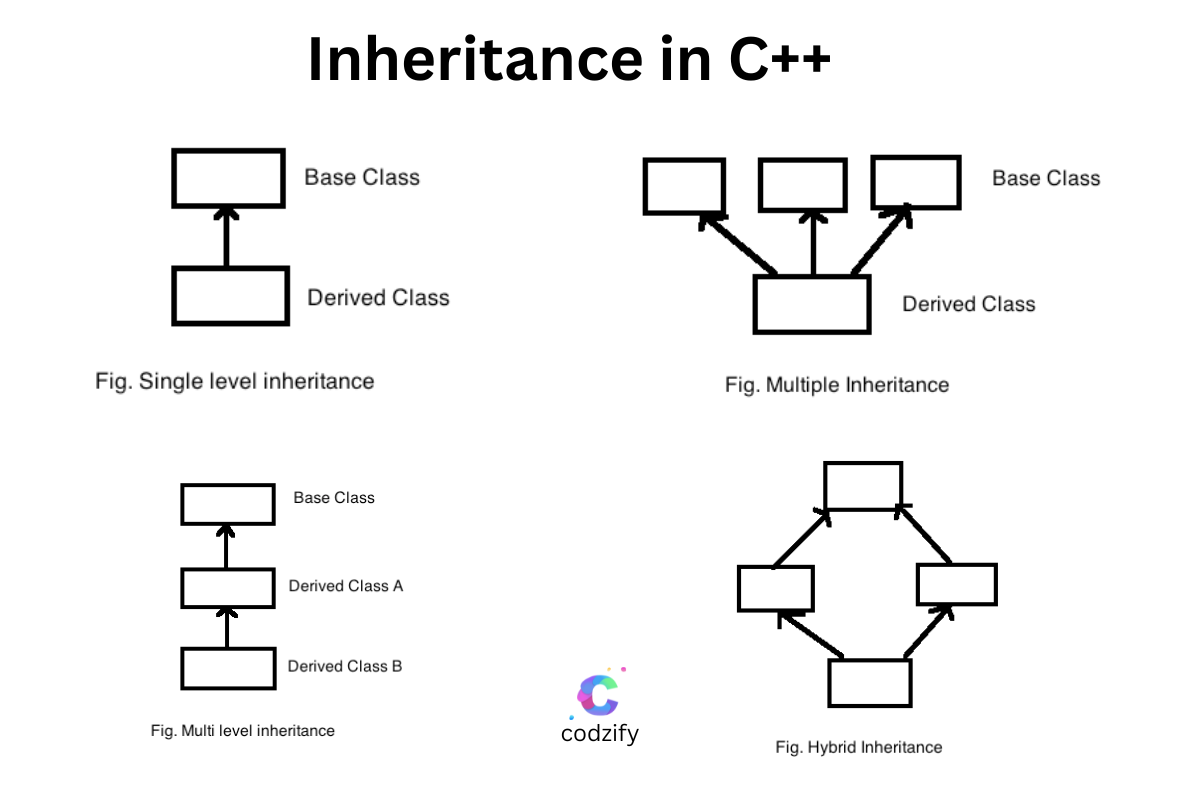
Table of Contents:
Introduction
Inheritance is a fundamental concept in C++ that enables a class to inherit properties and behaviors from another class, promoting code reuse and hierarchy within programs.

Syntax of Inheritance
In C++, inheritance syntax involves creating a derived class that inherits attributes and behaviors from a base class. Here's a basic representation:
// Base Class
class Base {
public:
void display() {
cout << "This is from the base class." << endl;
}
};
// Derived Class inheriting from Base
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void show() {
cout << "This is from the derived class." << endl;
}
};
Types of Inheritance
1. Single Inheritance
Single Level Inheritance involves deriving only one class from the base class. It establishes a straightforward parent-child relationship between two classes.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base {
public:
void display() {
cout <<"This is the Base class" << endl;
}
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void show() {
cout << "This is the Derived class" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Derived d;
d.display(); // Accessing Base class function
d.show(); // Accessing Derived class function
return 0;
}
Output:
This is the Base class This is the Derived class
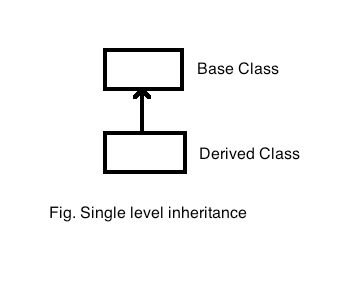
2. Multi-Level Inheritance
Multi-Level Inheritance signifies a chain of inheritance where one derived class becomes the base class for another derived class. It allows for multiple levels of derived classes.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
void displayA() {
cout << "This is class A" << endl;
}
};
class B : public A {
public:
void displayB() {
cout << "This is class B" << endl;
}
};
class C : public B {
public:
void displayC() {
cout << "This is class C" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
C c;
c.displayA(); // Accessing Class A method
c.displayB(); // Accessing Class B method
c.displayC(); // Accessing Class C method
return 0;
}
Output:
This is class A This is class B This is class C
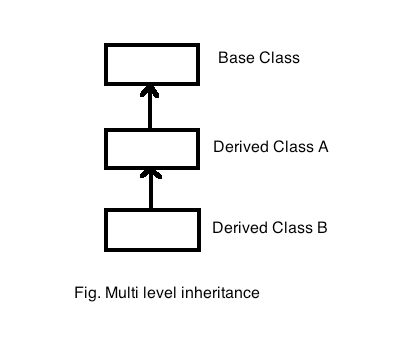
3. Hierarchical Inheritance
Hierarchical Inheritance occurs when multiple classes are derived from a single base class. It forms a hierarchical structure, branching out from a common base.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base {
public:
void display() {
cout << "This is the Base class" << endl;
}
};
class Derived1 : public Base {
public:
void show1() {
cout << "This is the first derived class" << endl;
}
};
class Derived2 : public Base {
public:
void show2() {
cout << "This is the second derived class" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Derived1 d1;
Derived2 d2;
d1.display(); // Accessing Base class function via first derived class
d1.show1(); // Accessing first derived class function
d2.display(); // Accessing Base class function via second derived class
d2.show2(); // Accessing second derived class function
return 0;
}
Output:
This is the Base class This is the first derived class This is the Base class This is the second derived class
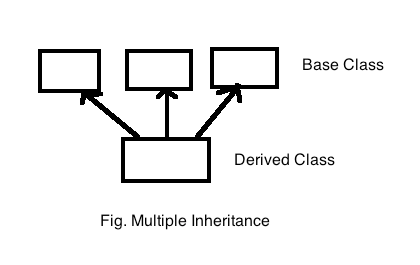
Multiple Inheritance
Multiple Inheritance occurs when a single class inherits properties and methods from multiple base classes. It provides a way to combine functionalities from different sources.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
void displayA() {
cout << "This is class A" << endl;
}
};
class B {
public:
void displayB() {
cout << "This is class B" << endl;
}
};
class C : public A, public B {
public:
void displayC() {
cout << "This is class C" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
C c;
c.displayA(); // Accessing Class A method
c.displayB(); // Accessing Class B method
c.displayC(); // Accessing Class C method
return 0;
}
Output:
This is class A This is class B This is class C
Hybrid Inheritance
Hybrid Inheritance is a combination of multiple inheritance types, encompassing multilevel, multiple, and hierarchical inheritance. It brings together various inheritance forms.

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
void displayA() {
cout << "This is class A" << endl;
}
};
class B : public A {
public:
void displayB() {
cout << "This is class B" << endl;
}
};
class C : public A {
public:
void displayC() {
cout << "This is class C" << endl;
}
};
class D : public B, public C {
public:
void displayD() {
cout << "This is class D" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
D d;
d.B::displayA(); // Accessing Class A method from class B
d.C::displayA(); // Accessing Class A method from class C
d.displayB(); // Accessing Class B method
d.displayC(); // Accessing Class C method
d.displayD(); // Accessing Class D method
return 0;
}
Output:
This is class A This is class A This is class B This is class C This is class D
Conclusion
Inheritance in C++ allows for the creation of complex class hierarchies, promoting code organization, and reuse. Understanding its types and syntax is crucial for building scalable and maintainable applications.
FAQ
1. What is Inheritance in C++?
In C++, Inheritance is a mechanism that allows a new class to inherit properties and behaviors (methods and attributes) from an existing class. It enables code reusability and establishes a hierarchical relationship between classes.
2. How does Single Level Inheritance work?
Single Level Inheritance involves only one base class and one derived class. The derived class inherits properties and behaviors from a single base class, forming a parent-child relationship.
3. What is Multi-Level Inheritance?
Multi-Level Inheritance refers to a chain of inheritance where a derived class inherits from a base class, and another class derives from this derived class. It creates a hierarchical order of classes.
4. Can a class be derived from multiple base classes in C++?
Yes, C++ supports Multiple Inheritance, allowing a derived class to inherit from more than one base class. It is essential to manage potential ambiguities and conflicts that can arise due to multiple inheritance.
5. What is Hybrid Inheritance?
Hybrid Inheritance is a combination of different types of inheritance (e.g., multiple, multilevel, or hierarchical). It incorporates multiple inheritance mechanisms within a single program, offering flexibility in class relationships.
