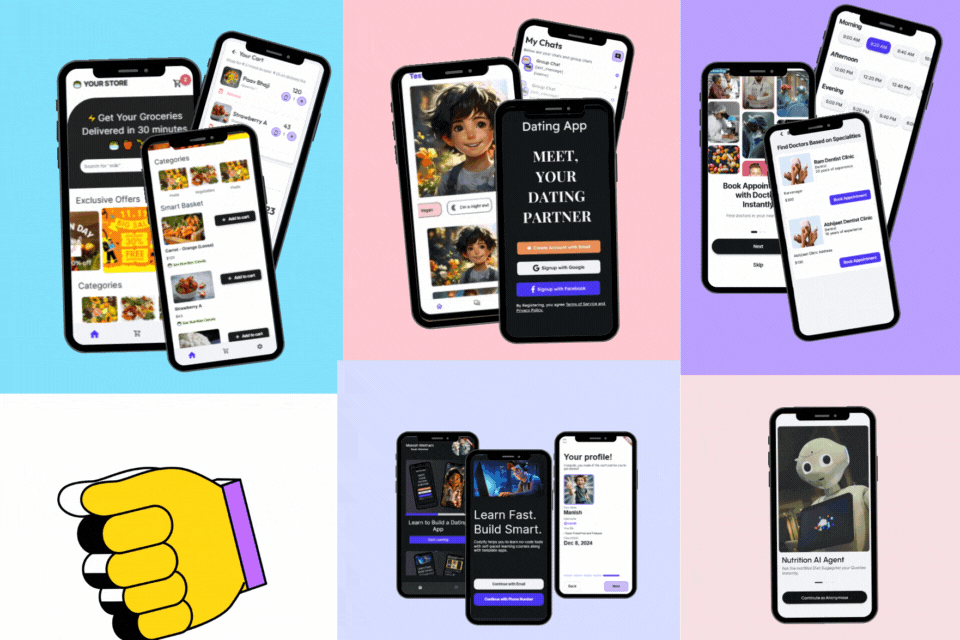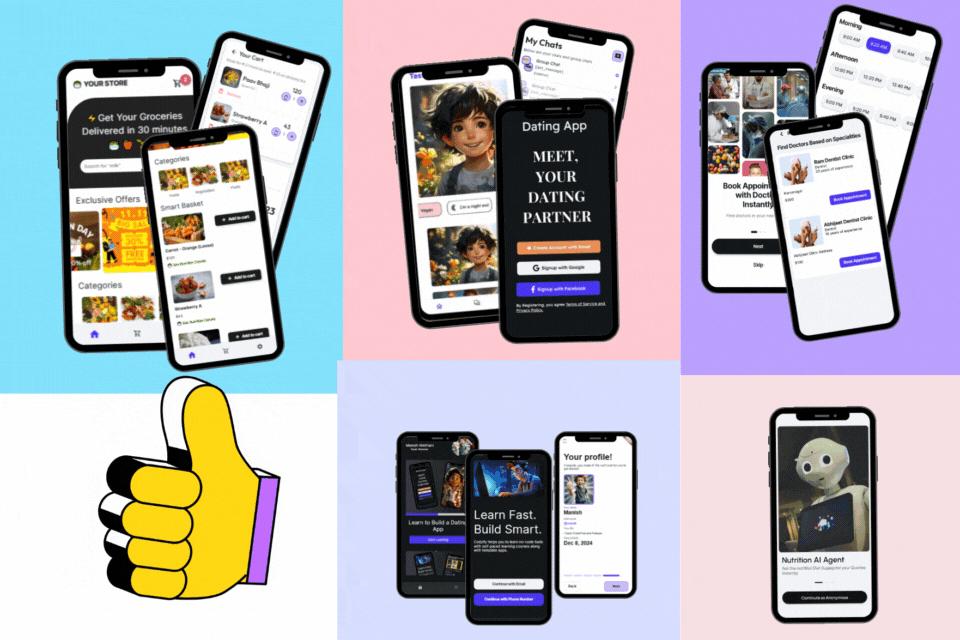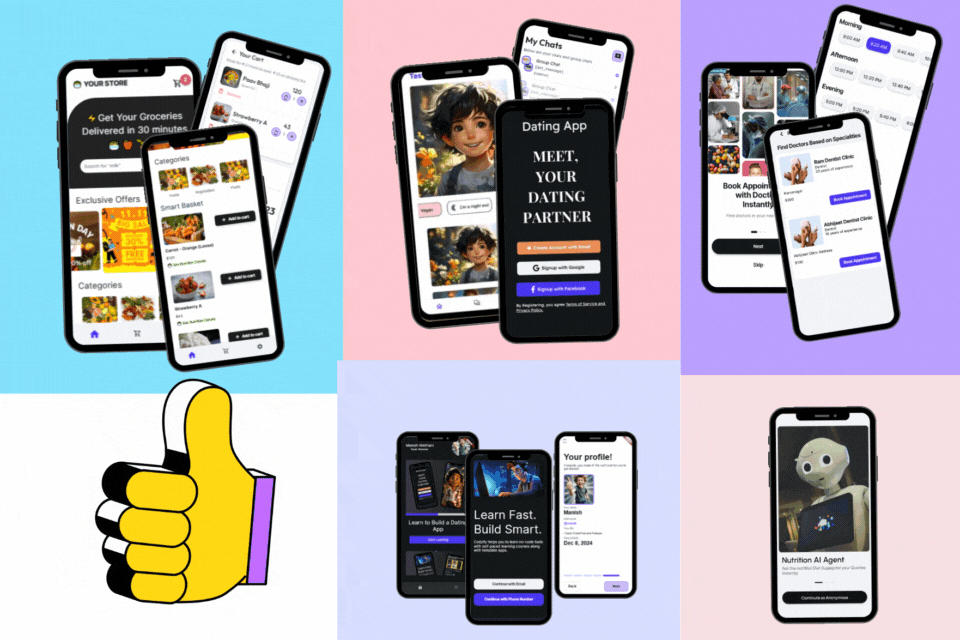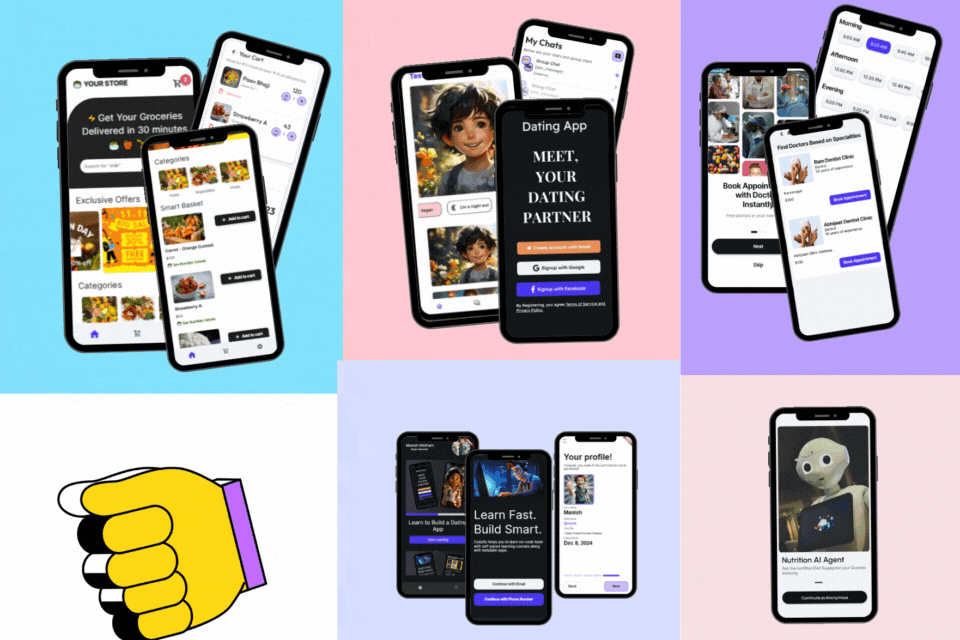
Learn to Build 5 Apps Without Coding using FlutterFlow
- Lifetime access to all the 5 FlutterFlow Courses
- Complete FlutterFlow training
- All future course updates
- Access via Codzify mobile app
- 24h 42m of Learning Content
- 5 FlutterFlow Courses at Codzify
- Access to Dating App Course, Grocery App Course, Courses App Course, FlutterFlow AI Agents Course, Doctor Appointment Booking Supabase Course.
- Clone Ready-Made Courses App instantly in FlutterFlow.
- 30-Day 100% Money-Back Guarantee.
Learn More