How to Reload View in SwiftUI: Beginners Guide with Code Examples and FAQs in 2023
Article by: Manish Methani
Last Updated: September 19, 2021 at 2:04pm IST
SwiftUI is a modern framework for building user interfaces on Apple platforms. It allows developers to create beautiful and interactive views with less code. One common problem that developers face is how to reload a view when its underlying data changes. In this tutorial, we will learn how to reload a view in SwiftUI using code and examples.
Introduction
SwiftUI provides a declarative way to create views, which means that you define what you want to display, and SwiftUI takes care of the rest. However, there are times when you need to reload a view when its underlying data changes. For example, you might have a list of items that can be deleted, and you need to update the view to reflect the changes. In this tutorial, we will explore different ways to reload a view in SwiftUI.
Understanding the Problem
Before we dive into the solutions, let's understand the problem first. When a view is created, SwiftUI generates the view hierarchy based on the data it receives. If the data changes, SwiftUI needs to be informed so that it can update the view hierarchy. In SwiftUI, the data is usually stored in a property, and when the property changes, the view should be reloaded.
Using @State Property Wrapper
One way to reload a view in SwiftUI is to use the @State property wrapper. @State is a property wrapper that allows you to store a value that can be modified. When a @State property changes, SwiftUI automatically reloads the view.
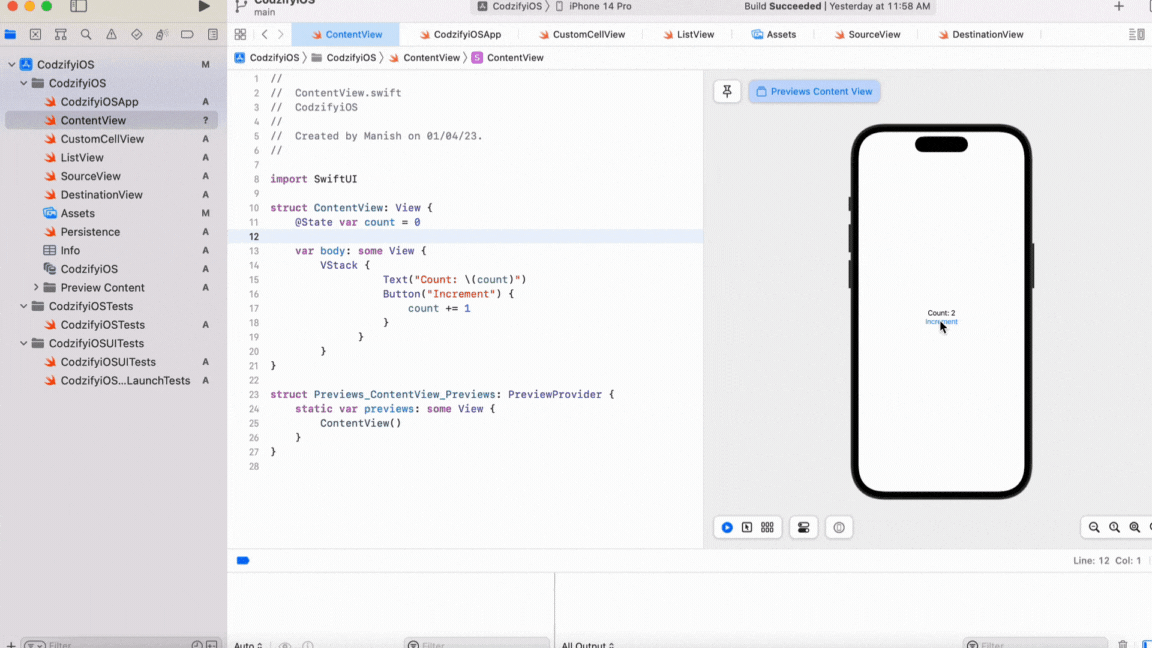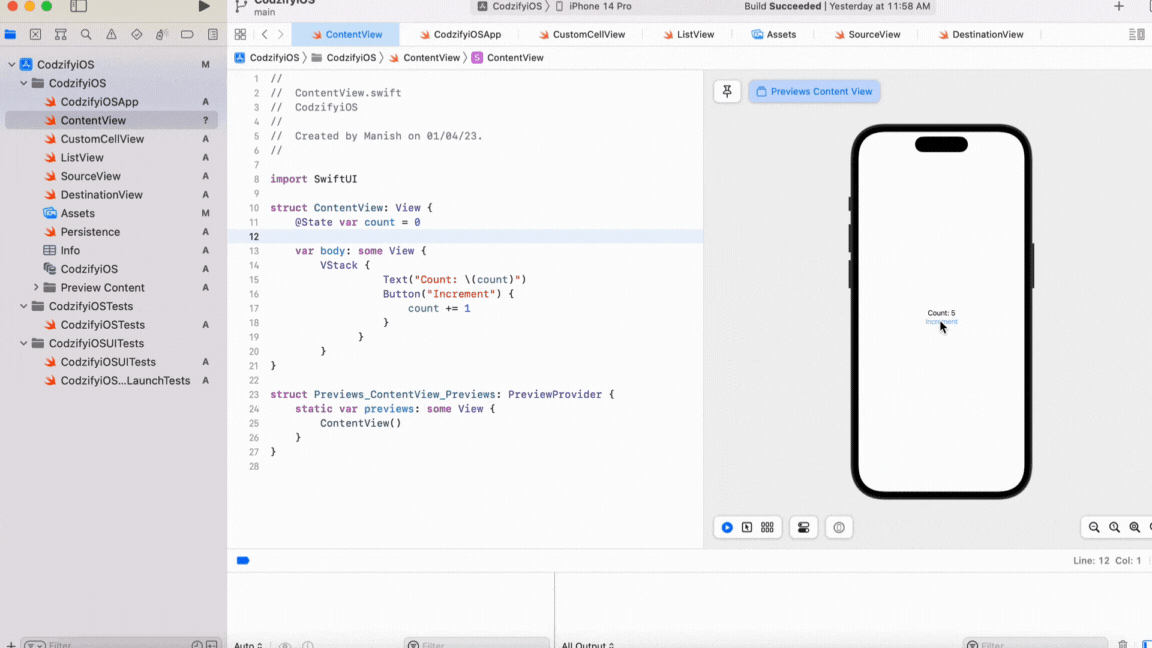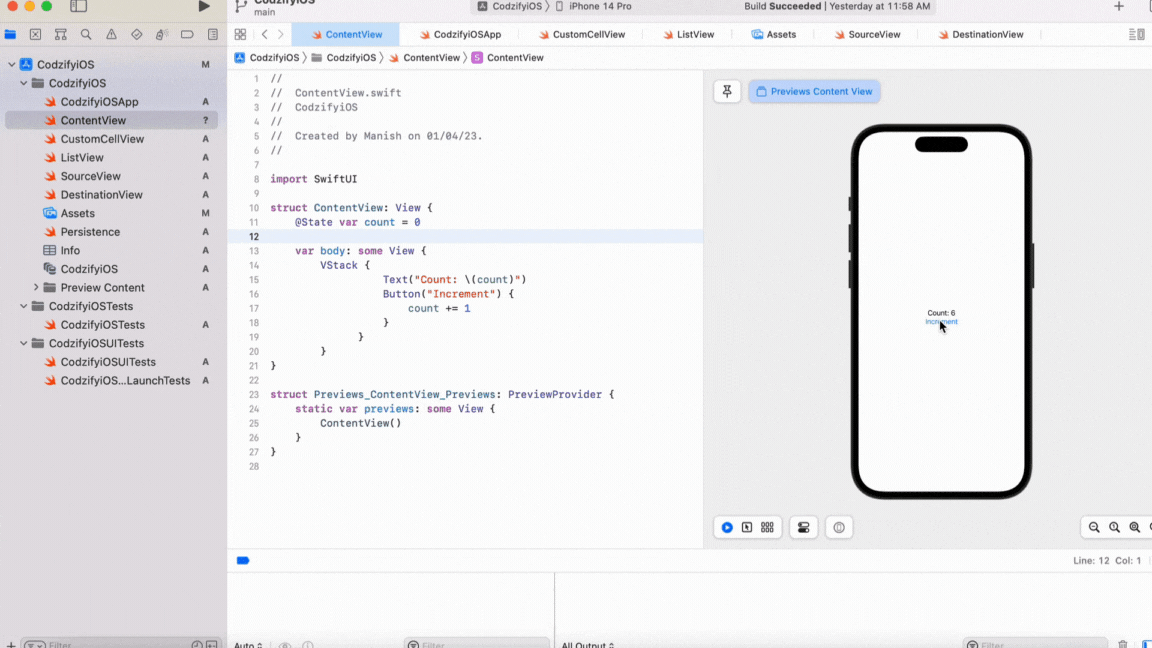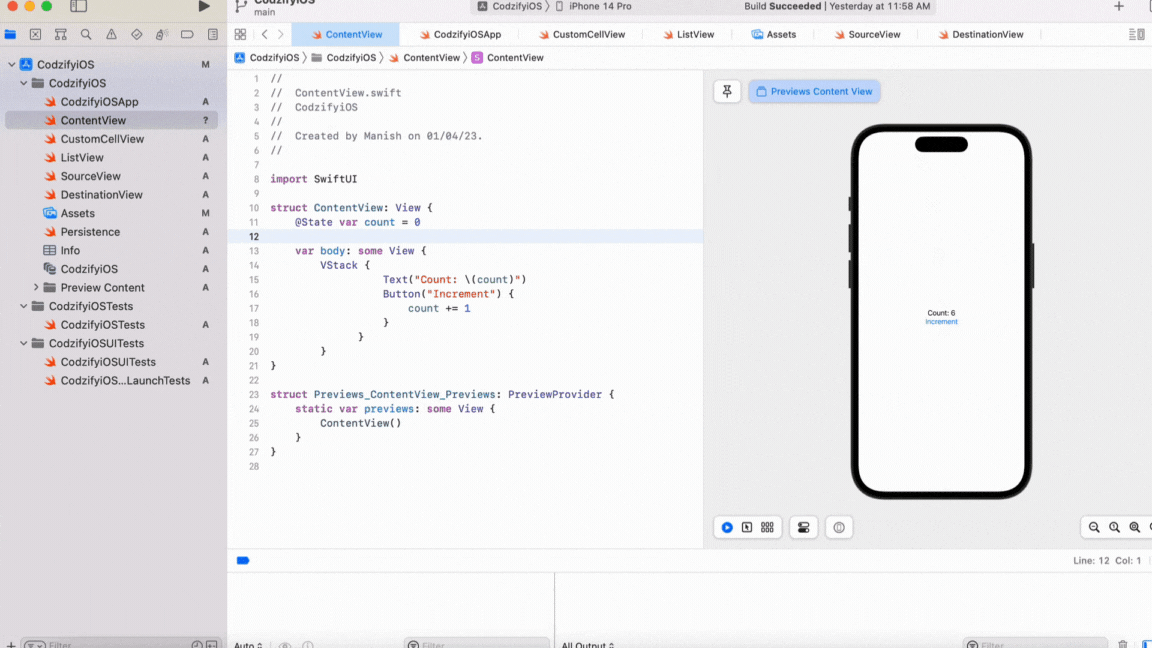
Let's take an example of a simple text view that displays a count. We will use a button to increment the count, and when the count changes, the text view should be updated.
struct ContentView: View {
@State var count = 0
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text("Count: (count)")
Button("Increment") {
count += 1
}
}
}
}
In this example, we have defined a @State property called count, which stores the value of the count. We have also defined a text view that displays the value of the count. When the button is pressed, the count is incremented, and the view is reloaded automatically.
Using ObservableObject and @Published Property Wrapper
Another way to reload a view in SwiftUI is to use the ObservableObject protocol and the @Published property wrapper. ObservableObject is a protocol that allows you to create a class that can be observed for changes. @Published is a property wrapper that allows you to mark a property as observable.
Let's take an example of a simple class that stores the count value. We will use this class as an observable object to update the view when the count changes.
class Counter: ObservableObject {
@Published var count = 0
func increment() {
count += 1
}
}
struct ContentView: View {
@ObservedObject var counter = Counter()
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text("Count: (counter.count)")
Button("Increment") {
counter.increment()
}
}
}
}
In this example, we have defined a class called Counter that conforms to the ObservableObject protocol. The class has a @Published property called count, which stores the value of the count. We have also defined a function called increment that increments the count. In the ContentView, we have defined an @ObservedObject property called counter, which observes changes to the Counter class. When the button is pressed, the count is incremented, and the view is reloaded automatically.

Using Combine and @Published Property Wrapper
If you want more control over the observation process, you can use Combine with the @Published property wrapper. Combine is a framework provided by Apple that allows you to work with asynchronous and event-driven programming.
Let's take an example of a simple class that stores the count value. We will use Combine to observe changes to the count property and update the view when the count changes.
import Combine
class Counter: ObservableObject {
@Published var count = 0
private var cancellable: AnyCancellable?
init() {
cancellable = $count
.sink { [weak self] _ in
self?.objectWillChange.send()
}
}
func increment() {
count += 1
}
}
struct ContentView: View {
@ObservedObject var counter = Counter()
var body: some View {
VStack {
Text("Count: (counter.count)")
Button("Increment") {
counter.increment()
}
}
}
}
In this example, we have defined a class called Counter that conforms to the ObservableObject protocol. The class has a @Published property called count, which stores the value of the count. We have also defined an init() method that uses the $count property to observe changes to the count property. When the count changes, the objectWillChange property is sent, which tells SwiftUI to update the view. In the ContentView, we have defined an @ObservedObject property called counter, which observes changes to the Counter class. When the button is pressed, the count is incremented, and the view is reloaded automatically.

Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have learned how to reload a view in SwiftUI using different methods. We have explored the @State property wrapper, the ObservableObject protocol with the @Published property wrapper, and the Combine framework with the @Published property wrapper. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and you should choose the one that best fits your use case.
FAQs
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a view in Swift UI?
A: A view is a basic building block of a user interface in Swift UI. It can be a simple visual element like a button or a more complex layout composed of several subviews.
Q: Why would I want to reload a view in Swift UI?
A: There are many situations where you might want to reload a view, such as when its content or appearance needs to be updated based on user input or changes in data.
Q: How do I reload a view in Swift UI?
A: You can reload a view in Swift UI by wrapping it in a NavigationView and using the onAppear modifier to trigger a reload when the view appears. Another approach is to use the @State property wrapper to track changes in the view's state and update the view accordingly.
Q: What is the NavigationView in Swift UI?
A: NavigationView is a container view in Swift UI that provides a standard navigation interface for your app. It includes a navigation bar at the top of the screen and a stack of views below it that can be navigated using push and pop operations.
Q: What is the onAppear modifier in Swift UI?
A: The onAppear modifier in Swift UI is used to attach a closure to a view that is called when the view appears on screen. This can be used to perform actions like reloading data or updating the views appearance.
Q: What is the @State property wrapper in Swift UI?
A: The @State property wrapper in Swift UI is used to store a value that can be mutated and trigger a view update when it changes. This is useful for tracking changes in the views state and updating the view accordingly.
Q: Are there any other ways to reload a view in Swift UI?
A: Yes, there are other approaches you can use to reload a view in Swift UI, such as using the ObservableObject protocol to create a model object that can publish changes to the view, or using the @Binding property wrapper to create a two-way binding between a parent and child view.
